Automotive NVH trends
22 May 2019
One of the most prominent trends in the automotive industry is electrification. By phasing out the internal combustion engine, our driving experience is changing. Noise and vibrations are no longer masked by this traditional driveline, which gives rise to new challenges in the field of noise & vibration engineering. A spread focus on various dominant noise sources and a significant increase in the frequency range of interest results in an overload of the traditional NVH engineering process with increasing cost and time-shortages.
Modular way of working
Most automotive NVH divisions are shifting to a more modular approach to cope with this. Therefore, component models (either simulated or measured) need to be of sufficient quality to be useful for NVH engineering/prediction in a multi-kHz frequency range. Also, active sources, such as the (e-)driveline and auxiliary systems, require to be characterized in such way that their vibration description is a property of the component itself.
The VIBES Methodology enables this modular way of working. Engineers are able to obtain modular descriptions of individual components which are valid in a large frequency range, typically up to 3000Hz or higher. Blocked Forces are being used as the independent quantities describing the active vibrations of the source. Component models and blocked forces are coupled together using Dynamic Substructuring.
With our DIRAC software, engineers can measure component models and obtain Virtual Points, ensuring compatibility with simulation models and with the added benefit of giving insight in the model quality and reliability. This allows for creating powerful hybrid assemblies and cherry-picking the best component modeling approach on a case-by-case basis.
Our SOURCE solution allows for obtaining independent blocked forces. By combining DIRAC and SOURCE, we combine measurement and simulation and significantly improve the quality of sound and vibration prediction for automotive assemblies.
Implementations
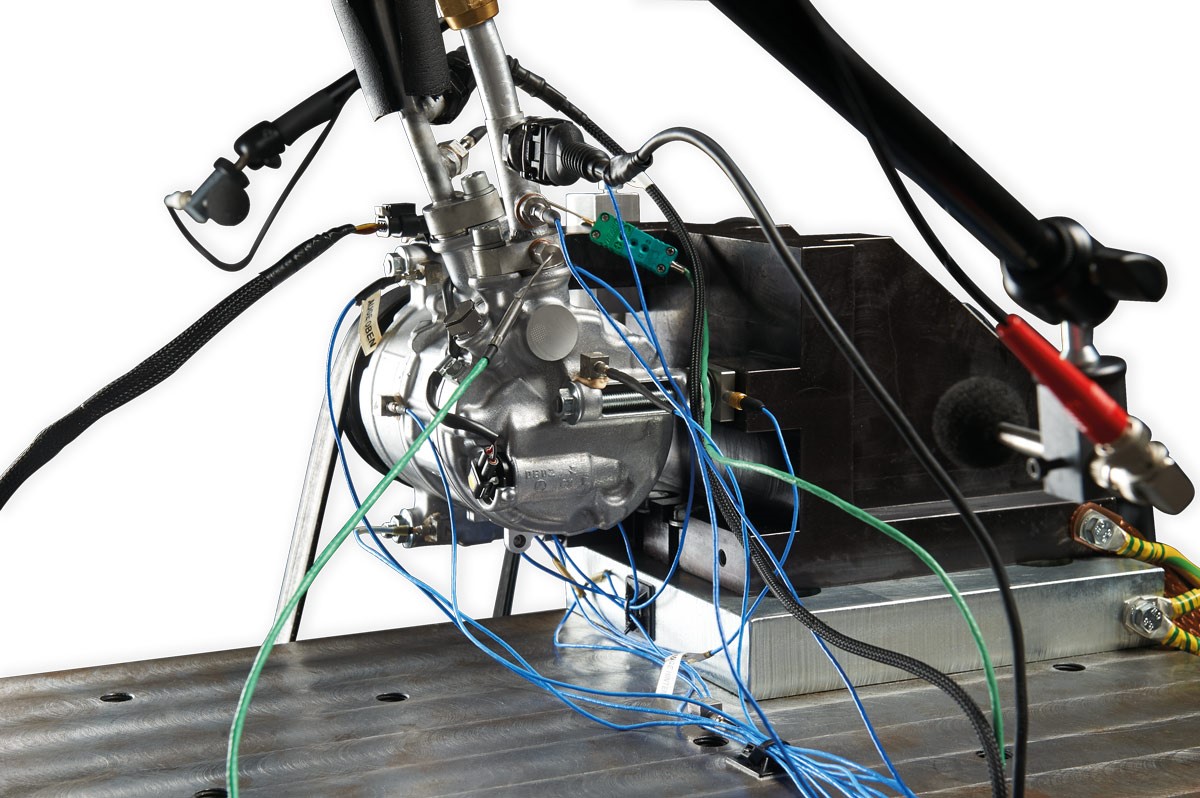
We have successfully applied our methodology and software in the industry. A recent project concerned the analysis of an e-compressor as a noise source for an OEM of electric vehicles. As vehicle prototypes were not available in this stage of development, the e-compressor was tested on a component test bench. DIRAC was used to prepare, measure and analyze the FRF measurements. While performing the actual measurement, every single measurement point was evaluated on-the-fly using Virtual Point technology and the associated quality indicators, leading to much higher quality than possible with traditional measurement workflows.
The source characterisation was consequently performed in SOURCE, combining the virtual point FRF matrix and the operational test-bench measurements. Blocked forces and moments were obtained that are perfectly transferable to the vehicle, owing to the fact that the virtual points collocate with the actual connection points in the vehicle.
The key results in the project:
- Using the measured blocked forces, the OEM was able to predict the NVH performance of the compressor in the vehicle – through a hybrid simulation combining test data and FE models.
- Based on the simulations, the customer decided to add an additional isolation stage at the mounts, saving ~15 dB on interior noise.
- The project demonstrated the power of a fully modular NVH approach, with a supplier in Europe and the predictions performed overseas at the OEM engineering department.
With the VIBES Methodology and its software products, late-phase sound and vibration troubleshooting is avoided, fewer iterative design cycles are needed, saving time and resources. All-in-all we’re making reliable full-vehicle models available earlier in the development process.
Do you like to find out how your NVH challenges on electrification or modular approach can be met? Get in touch and we are happy to consult. info@vibestechnology.com or click on the contact us button.